The Effectiveness of PjBL-STEAM Using GeoAI Media: Junior High School Students' Creative Thinking Skills
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51574/ijrer.v4i4.3788Keywords:
Creative Thinking Skills, GeoAI, Junior High School, PjBL-STEAM, Science LearningAbstract
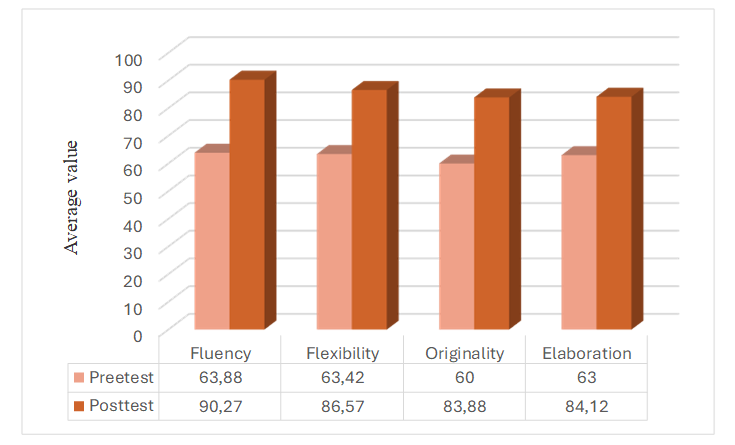
The problem identified in this study stemmed from the condition of science learning, which remained limited to the learning model and media used, resulting in less effectiveness in developing creativity. Therefore, this study was conducted to test the effectiveness of the Project Based Learning (PjBL) model integrated with the Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics (STEAM) approach using Geospatial Information System Artificial Intelligence (GeoAI) media in improving students' creative thinking skills. This study used a mixed-methods design with an embedded experimental model, where the data collection techniques were carried out through pre-research interviews, pretests and posttests, questionnaires, and interviews after the intervention. The research sample consisted of second-semester students from class VIII at Public Junior High School 1 Weru. We processed the data using normality tests, homogeneity tests, paired sample t-tests, independent sample t-tests, and N-Gain tests. The results showed a significant increase in creative thinking skills in the experimental class. The improvement was evidenced by the results of the average pretest score of 66.32, then the posttest increased to 90.44, with a very significant difference compared to the control class. The N-Gain test also recorded improvements, with an average score of 0.69 in the moderate category. This finding is reinforced by qualitative data from questionnaires and interviews, which showed a very positive response from students to the GeoAI-assisted PjBL-STEAM model, achieving an average score of 75.99% out of a maximum score of 100%.
References
Afifah, S., Mudzakir, A., & Nandiyanto, A. B. D. (2022). How to calculate paired sample t-test using SPSS software: From step-by-step processing for users to the practical examples in the analysis of the effect of application anti-fire bamboo teaching materials on student learning outcomes. Indonesian Journal of Teaching in Science, 2(1), 81-92. https://ejournal.upi.edu/index.php/ijotis/article/view/45895
Ardiyansah, E., Rinto, R., & Fatnah, N. (2024). Pengaruh model pjbl-stem menggunakan algodoo terhadap pembelajaran ipa dalam peningkatan keterampilan berpikir kritis dan keterampilan berpikir kreatif. Inkuiri: Jurnal Pendidikan IPA, 13(2), 160-167. https://doi.org/10.20961/inkuiri.v13i2.91876
Baidal-Bustamante, E., Mora, C., & Alvarez-Alvarado, M. S. (2023). STEAM project-based learning approach to enhance teaching-learning process in the topic of pascal’s principle. IEEE Transactions on Education, 66(6), 632-641. https://doi.org/10.1109/TE.2023.3283850
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2021). Thematic analysis: A practical guide to a rigorous method. Journal of Qualitative Research, 26(1), 22–38. https://www.torrossa.com/it/resources/an/5282292
Chen, S. Y., Lai, C. F., Lai, Y. H., & Su, Y. S. (2022). Effect of project-based learning on development of students’ creative thinking. The International Journal of Electrical Engineering & Education, 59(3), 232-250. https://doi.org/10.1177/0020720919846808
Chistyakov, A. A., Zhdanov, S. P., Avdeeva, E. L., Dyadichenko, E. A., Kunitsyna, M. L., & Yagudina, R. I. (2023). Exploring the characteristics and effectiveness of project-based learning for science and STEAM education. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 19(5), em2256. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/13128
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2017). Mixed methods research. In Research methods in education (pp. 31-50). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315456539-2
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2017). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Sage publications.
de Souza, R. R., Toebe, M., Mello, A. C., & Bittencourt, K. C. (2023). Sample size and Shapiro-Wilk test: An analysis for soybean grain yield. European Journal of Agronomy, 142, 126666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2022.126666
Diana, N., & Sukma, Y. (2021). The effectiveness of implementing project-based learning (PjBL) model in STEM education: A literature review. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1882, No. 1, p. 012146). IOP Publishing.
González-Pérez, L. I., & Ramírez-Montoya, M. S. (2022). Components of Education 4.0 in 21st century skills frameworks: systematic review. Sustainability, 14(3), 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031493
Indahwati, S. D., Rachmadiarti, F., & Hariyono, E. (2023). Integration of PJBL, STEAM, and learning tool development in improving students' critical thinking skills. IJORER: International Journal of Recent Educational Research, 4(6), 808-818. https://doi.org/10.46245/ijorer.v4i6.434
Jannah, D. R. N., & Atmojo, I. R. W. (2022). Media digital dalam memberdayakan kemampuan berpikir kritis abad 21 pada pembelajaran IPA di sekolah dasar. Jurnal Basicedu, 6(1), 1064–1074. https://doi.org/10.31004/basicedu.v6i1.2124
Janowicz, K., Gao, S., McKenzie, G., Hu, Y., & Bhaduri, B. (2020). GeoAI: spatially explicit artificial intelligence techniques for geographic knowledge discovery and beyond. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 34(4), 625-636. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2019.1684500
Lee, J. (2023). Beyond geospatial inquiry—How can we integrate the latest technological advances into geography education?. Education Sciences, 13(11), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13111128
Lou, S. J., Chou, Y. C., Shih, R. C., & Chung, C. C. (2017). A study of creativity in CaC2 steamship-derived STEM project-based learning. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 13(6), 2387-2404. https://doi.org/10.12973/eurasia.2017.01231a
Lu, S. Y., Lo, C. C., & Syu, J. Y. (2022). Project-based learning oriented STEAM: The case of micro–bit paper-cutting lamp. International Journal of Technology and Design Education, 32(5), 2553-2575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-021-09714-1
Mufida, S. N., Sigit, D. V., & Ristanto, R. H. (2020). Integrated project-based e-learning with science, technology, engineering, arts, and mathematics (PjBeL-STEAM): its effect on science process skills. Biosfer: Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi, 13(2), 183-200. https://doi.org/10.21009/biosferjpb.v13n2.183-200
Pérez Torres, M., Couso Lagarón, D., & Marquez Bargalló, C. (2023). Evaluation of STEAM project-based learning (STEAM PBL) instructional designs from the STEM practices perspective. Education Sciences, 14(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14010053
Retno, R. S., Purnomo, P., Hidayat, A., & Mashfufah, A. (2025). Conceptual framework design for STEM-integrated project-based learning (PjBL-STEM) for elementary schools. Asian Education and Development Studies, 14(3), 579-604. https://doi.org/10.1108/AEDS-08-2024-0188
Stkipsubang. (2022). Kompetensi 4C dalam implementasi Kurikulum Merdeka di sekolah dasar. Jurnal Didaktik: Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan, 6(2), 114-122. https://journal.stkipsubang.ac.id/index.php/didaktik/article/download/1136/1045
Sukackė, V., Guerra, A. O. P. D. C., Ellinger, D., Carlos, V., Petronienė, S., Gaižiūnienė, L., ... & Brose, A. (2022). Towards active evidence-based learning in engineering education: A systematic literature review of PBL, PjBL, and CBL. Sustainability, 14(21), 13955. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142113955
Sukmawati, E., Imanah, N. D. N., & Rantauni, D. A. (2023). Implementation and challenges of project-based learning of STEAM in the university during the pandemic: A systematic literature review. JINoP (Jurnal Inovasi Pembelajaran), 9(1), 128-139. https://doi.org/10.22219/jinop.v9i1.25177
Thornhill-Miller, B., Camarda, A., Mercier, M., Burkhardt, J. M., Morisseau, T., Bourgeois-Bougrine, S., ... & Lubart, T. (2023). Creativity, critical thinking, communication, and collaboration: Assessment, certification, and promotion of 21st century skills for the future of work and education. Journal of Intelligence, 11(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence11030054
Usery, E. L., Arundel, S. T., Shavers, E., Stanislawski, L., Thiem, P., & Varanka, D. (2022). GeoAI in the US Geological Survey for topographic mapping. Transactions in GIS, 26(1), 25–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/tgis.12830
VoPham, T., Hart, J. E., Laden, F., & Chiang, Y. Y. (2018). Emerging trends in geospatial artificial intelligence (geoAI): potential applications for environmental epidemiology. Environmental Health, 17(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-018-0386-x
Yang, K. K., Lee, L., Hong, Z. R., & Lin, H. S. (2016). Investigation of effective strategies for developing creative science thinking. International Journal of Science Education, 38(13), 2133-2151. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500693.2016.1230685
Zayyinah, Z., Erman, E., Supardi, Z. A., Hariyono, E., & Prahani, B. K. (2022). STEAM-integrated project based learning models: Alternative to improve 21st century skills. In Eighth Southeast Asia Design Research (SEA-DR) & the Second Science, Technology, Education, Arts, Culture, and Humanity (STEACH) International Conference (SEADR-STEACH 2021) (pp. 251-258). Atlantis Press.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ajeng Ajeng, Rinto Rinto, Nurwanti Fatnah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.









1.png)













